MIT6.5840 2024 Spring Lab1
前言
本文主要作为笔记使用,这次实验基本是边查GO的语法边做的,所以代码写的不够优雅,无法充分发挥GO的一些特性,因此本文的代码实现有很大的优化空间,欢迎各位大佬指正,希望本文能给一些正在学习的小伙伴提供一些思路。最后希望小伙伴们不要抄代码,可以看本文前几个部分参考思路然后自己实现,本文的代码适合自己写完后交流学习用而不是copy用。
前置知识
GO
这里主要列举我在代码实现时用到的GO的一些知识。
- goroutine
可以简单理解线程,Go执行的时候会将goroutine的任务分配给CPU执行。func hello(name string){ fmt.Println("你好",name) } func main(){ name := "moyoj" //此时会启动一个goroutine去单独执行该函数,程序与主函数是同时执行的 go hello(name) }如果用C++来表示的话,类似于下面代码
void hello(string name){ std::cout<<"你好 "<<name<<std::endl; } int main(){ std::string name = "moyoj"; std::thread t(hello,name); t.detach();//分离线程 return 0 } - channel
可以理解成线程安全的队列,在不加锁的情况下,不同goroutine安全访问的队列。func main(){ channame := make(chan int,100) //声明一个传递整型的通道,缓冲大小100 channame <- 114514 //把114514发送到channel中 res := <- channame //从channel中接收114514 } - 方法定义
type Test struct{ name string password string } //定义一个recriver为值传递的方法,参数为string类型,返回值为string类型 func (tname Test) VChangeName(name string) string{ fmt.Println("名字改变前:",tname.name) tname.name = name //因为tname是值传递这里修改不影响外面调用者 return tname.name } //定义一个recriver为指针传递的方法,参数为string类型,返回值为string类型 func (tname *Test) PChangeName(name string) string{ fmt.Println("名字改变前:",tname.name) tname.name = name //tname是指针传递,会改变外部调用者的值 return tname.name } func main(){ test := Test{"moyoj","99999"} name := test.VChangeName("baka!") fmt.Println(test.name,pwd) //moyoj 99999 name = test.PChangeName("baka!") fmt.Println(test.name,pwd) //baka! 99999 }指针传递可以类比于C++的以下实现:
class Test{ public: std::string name; std::string password; Test(std::string name_,std::string pwd):name(name_),password(pwd) { } std::string ChangeName(string name_){ std::cout<<"改变名字前 "<<name<<std::endl; name = name_; return name; } }; int main(){ Test test("moyoj","99999"); std::string name = test.ChangeName("baka!"); std::cout<<test.name<<" "<<test.password<<std::endl; //baka! 99999 return 0; }
MapReduce论文
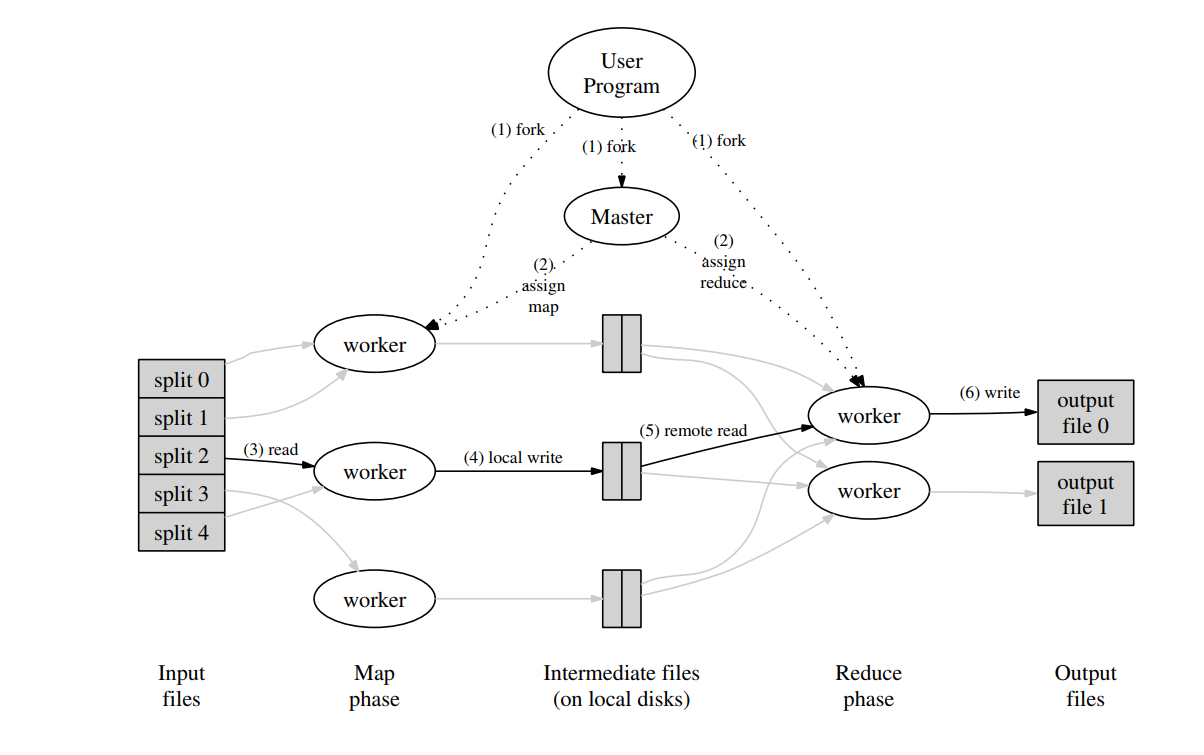
本实验主要的核心是这篇论文的执行流程图,Master用于分配Map或Reduce任务给不同的节点并行处理,Map会从一个或者多个文件获取数据进行map任务,产生中间文件,所有Map任务完成后,Reduce会从中间文件获取数据进行Reduce任务,进而写入输出文件。对于WordCount这个实验来说,Map任务会从文件中的英文句子分割出单词,以”word 1″的形式输入到中间文件中,其中word可以理解为key值,”1″是value值,key值可能会重复这没关系,Reduce从中间文件获取n多个”word 1″形式的键值对,并对同一种key进行合并,假设有m个key等于hello的键值对,最后合并后就会变成”hello m”并输出到输出文件。(上述的”word 1″是指将key为word,value为1的键值对写入文件,具体实际上是用json格式写的)
思路
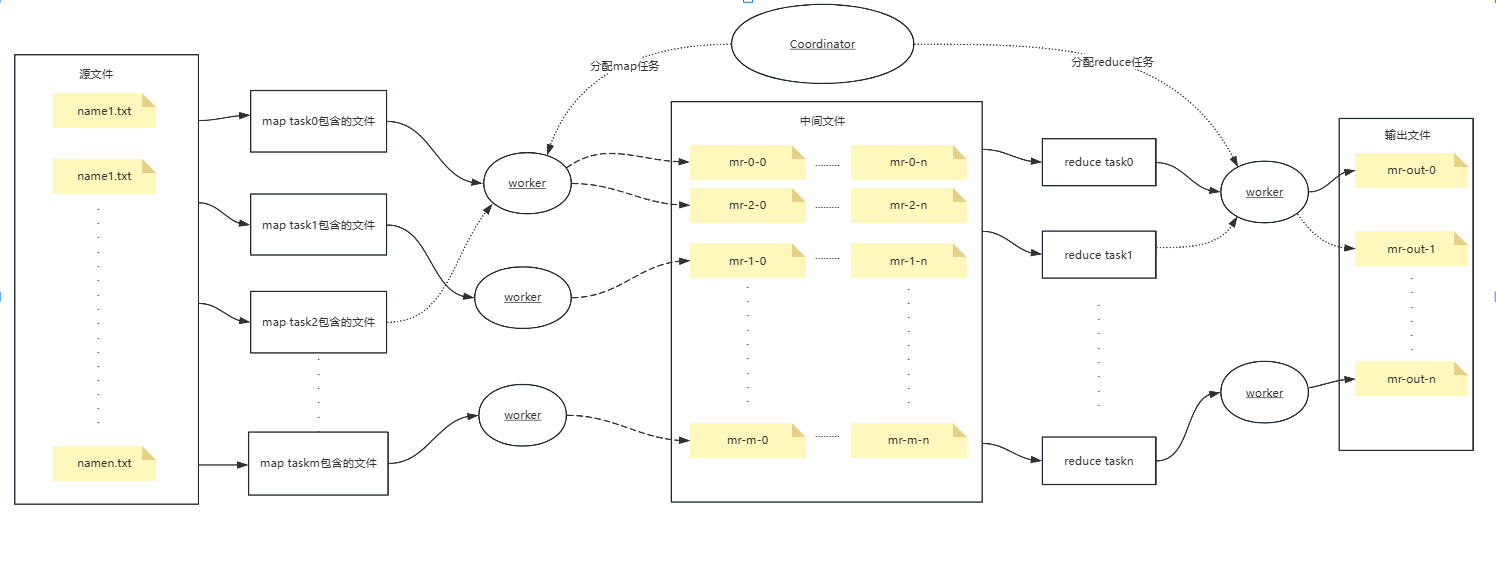
任务分配与文件生成方式
本实验主要分为协调节点和工作节点,其实对应了三个进程,协调节点启动时会初始化taskmap,存储任务号和该任务要处理的文件名,工作节点向协调节点发起任务请求,协调节点分返回任务号的文件列表和任务类型(map or reduce),工作节点根据任务类型处理文件列表,map任务会根据任务号id和word经过哈希后生成范围在[0,n]的序号i将”word 1″写入文件名为”mr-id-i”的文件中,reduce任务则会根据任务号id获取文件名为”mr-*-id”的文件(*通配符代表任何字符)进行统计计数,之后输出到名为”mr-out-id”的输出文件中。
程序执行流程框架
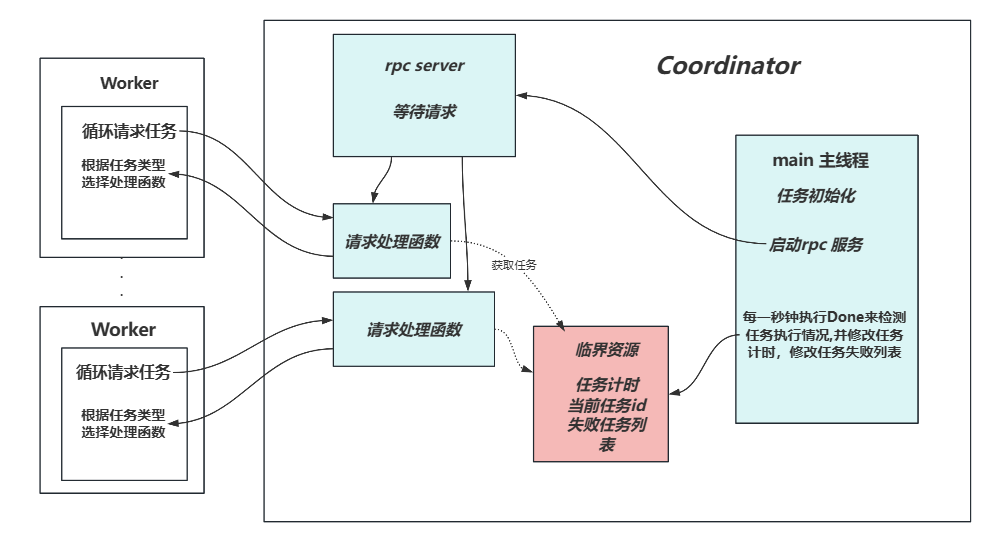
本流程图未必严谨,主要是为了说明一个进程内哪些goroutine或者线程是并发执行的,同一个背景颜色就说明他们是并发执行的,访问临界资源需要考虑data race。
先启动协调节点主进程初始化任务列表等资源,将不同文件划分到不同的map任务下,之后启动rpc服务等待工作节点请求任务,此时rpc服务和主线程是并发执行,之后主线程每sleep一秒就醒来检查一下当前任务阶段是否全部执行完成,之后继续检查超时任务,超时的任务放入失败任务队列,正在执行的任务时间计数加1。
继续说请求处理函数,rpc服务接收到请求后会执行请求处理函数,先检查请求Worker回复的TASKREPLYID,如果为-1则第一次请求,如果不是说明该Worker已经完成上次请求,根据此ID删除任务计时表对应项,之后请求处理函数会从临界资源获取要执行的任务,这个任务可能是从还未执行的任务里获得的,也有可能是在失败任务队列里获取的,之后将未来要执行的任务放入任务计时表,然后响应请求(填reply就行)。至于工作线程,获取任务请求响应后执行相应的map或reduce处理函数即可。
执行完map后,主线程会初始化reduce任务表,之后继续执行reduce任务。
代码实现
RPC
type WorkRequest struct {
TASKREPLYID int //上次完成的任务ID
}
type WorkerReply struct {
WORKTYPE int //任务类型0代表map 1代表reduce
REDUCENUM int //reduce任务的个数
TASKID int //任务ID
FILELIST []string //需要关注的文件名
}
Coordinator
公共资源
//协调节点结构体
type Coordinator struct {
// Your definitions here.
TaskTimeCount map[int]int //正在执行的任务的时间计数 pair TaskID:count
TaskMap map[int][]string //任务表
FailTask chan int //执行失败任务表
TaskIndex int //当前任务ID表的下标
TaskTye int //当前执行的任务类型
ReduceNum int //reduce任务数量,中间文件后缀可能的最大值,中间文件后缀是mod ReduceNum得到的
ChooseTaskMutex sync.Mutex //选择任务时加锁
TimeCountMutex sync.Mutex //不同线程删除计时器增加计时器时需要互斥
}
主线程
//初始化协调节点的数据结构,启动rpc服务
func MakeCoordinator(files []string, nReduce int) *Coordinator {
c := Coordinator{}
filecount := len(files)
numpertask := filecount/nReduce + 1 //每个任务处理的文件数 这里假设为 文件数/reduce数 + 1
c.TaskMap = make(map[int][]string, filecount/numpertask+1)
for i := 0; i < len(files); i++ {
curid := i / numpertask
_, exist := c.TaskMap[curid]
if !exist {
c.TaskMap[curid] = make([]string, 0, filecount)
}
c.TaskMap[curid] = append(c.TaskMap[curid], files[i])
}
fmt.Print(c.TaskMap)
c.TaskIndex = 0
c.FailTask = make(chan int, filecount)
c.TaskTimeCount = map[int]int{}
c.TaskTye = 0
c.ReduceNum = nReduce
c.server()
return &c
}
//检测任务完成情况
func (mpc *Coordinator) IsComplete() bool {
flag := false
//未执行任务为空,失败任务为空,正在执行的任务为空,才说明结束
mpc.ChooseTaskMutex.Lock()
maxlen := mpc.ReduceNum
if len(mpc.TaskMap) > maxlen {
maxlen = len(mpc.TaskMap)
}
if mpc.TaskIndex == maxlen && len(mpc.FailTask) == 0 && len(mpc.TaskTimeCount) == 0 {
flag = true
}
mpc.ChooseTaskMutex.Unlock()
return flag
}
//Reduce任务初始化函数,执行完map任务后会执行,来分配任务
func (mpc *Coordinator) ReduceInit() {
mpc.TaskMap = nil
mpc.TaskMap = make(map[int][]string, mpc.TaskIndex) //每个任务处理的文件数最多为,map任务数
mpc.TaskIndex = 0
mpc.TaskTimeCount = map[int]int{}
mpc.TaskTye = 1
i := 0
files, err := ioutil.ReadDir("./")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("读取目录失败")
return
}
//获取文件名为mr-*-i的文件,作为任务i,也有可能map并没产生后缀为i的文件,这没关系,直接返回空文件列表就行了(嘿嘿偷个懒)
for i = 0; i < mpc.ReduceNum; i++ {
pattern := "mr-*-" + strconv.Itoa(i)
for _, file := range files {
flag, err := filepath.Match(pattern, file.Name())
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("模式匹配失败")
}
if flag {
mpc.TaskMap[i] = append(mpc.TaskMap[i], file.Name())
}
}
}
fmt.Println(mpc.TaskMap)
}
//原代码中的Done函数,就是每1s需要检查一下任务处理状态
func (c *Coordinator) Done() bool {
ret := false
if c.IsComplete() {//当前任务是否执行完成
if c.TaskTye == 1 { //reduce完直接返回了
//关闭channel
close(c.FailTask)
return true
}
//只是map完,还需要处理reduce
//reduce预处理前先加锁,别回应任务请求
c.ChooseTaskMutex.Lock()
c.ReduceInit()
c.ChooseTaskMutex.Unlock()
}
c.TimeCountMutex.Lock()
for task, time := range c.TaskTimeCount {
time++
if time > 10 { //超时10s,因为这个函数每一秒执行一次,每次执行都把正在执行的任务计时加1
c.FailTask <- task //放入失败任务节点
delete(c.TaskTimeCount, task) //删除计时器
continue
}
c.TaskTimeCount[task] = time //还在执行的任务计时加1
}
c.TimeCountMutex.Unlock()
return ret
}
请求响应线程
//选择一个任务
func (mpc *Coordinator) ChooseTask() ([]string, int) {
res := []string{}
taskid := -1
//如果某任务id对应任务可以是空
if mpc.TaskIndex < len(mpc.TaskMap) || mpc.TaskIndex<mpc.ReduceNum {
taskid = mpc.TaskIndex
mpc.TaskIndex++
}
if taskid == -1 { //未执行任务列表为空,那就检查失败任务列表
if len(mpc.FailTask) > 0 {
taskid = <-mpc.FailTask
}
}
if taskid != -1 { //成功获取任务
res = mpc.TaskMap[taskid]
mpc.TimeCountMutex.Lock()
mpc.TaskTimeCount[taskid] = 0
mpc.TimeCountMutex.Unlock()
fmt.Println("[", taskid, "]任务被分配")
}
return res, taskid
}
//请求处理函数
func (mpc *Coordinator) HandleRequest(request *WorkRequest, response *WorkerReply) error {
replyid := request.TASKREPLYID
if replyid != -1 {
mpc.TimeCountMutex.Lock()
fmt.Println(replyid,"执行完成收到回复,删除定时器")
delete(mpc.TaskTimeCount, replyid)
mpc.TimeCountMutex.Unlock()
}
//临界资源过多,选择线程时直接加锁,同一时刻最多为一个请求选择任务
mpc.ChooseTaskMutex.Lock()
response.FILELIST, response.TASKID = mpc.ChooseTask()
response.REDUCENUM = mpc.ReduceNum
response.WORKTYPE = mpc.TaskTye
mpc.ChooseTaskMutex.Unlock()
return nil
}
Worker
排序方法集
//这个实际上课程给定代码就有
type ByKey []KeyValue
func (a ByKey) Len() int { return len(a) }
func (a ByKey) Swap(i, j int) { a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i] }
func (a ByKey) Less(i, j int) bool { return a[i].Key < a[j].Key }
rpc请求
func Worker(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue,
reducef func(string, []string) string) {
taskid := -1
for {
request := WorkRequest{}
request.TASKREPLYID = taskid //上次执行的任务ID,这次请求顺便带回去
response := WorkerReply{}
ok := call("Coordinator.HandleRequest", &request, &response)
if ok {
taskid = response.TASKID
if taskid == -1 { //没任务
continue
}
worktype := response.WORKTYPE
reducen := response.REDUCENUM
files := response.FILELIST
if worktype == 0 {
HandMap(mapf, files, taskid, reducen)
} else {
HandReduce(reducef, files, taskid)
}
}
}
}
Map任务处理
func HandMap(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue, files []string, taskid int, reducen int) {
if len(files) == 0 {
return
}
intermediate := []KeyValue{}
//获取map函数统计的字符结果
for _, filename := range files {
file, err := os.Open(filename)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot open %v", filename)
}
content, err := ioutil.ReadAll(file)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot read %v", filename)
}
file.Close()
kva := mapf(filename, string(content))
intermediate = append(intermediate, kva...)
}
sort.Sort(ByKey(intermediate)) //我的实现这里其实可以不排序
//记录某个文件对应的文件描述符
namemap := map[string]*os.File{}
//组合前缀
namepre := "mr-" + strconv.Itoa(taskid) + "-"
i := 0
for i < len(intermediate) {
j := i + 1
for j < len(intermediate) && intermediate[j].Key == intermediate[i].Key {
j++
}
curkey := intermediate[i].Key //获取当前这组的Key
nameSuffix := strconv.Itoa(ihash(curkey) % reducen) //名字后缀
name := namepre + nameSuffix //前缀+后缀
openfile, exist := namemap[name]
if !exist { //该文件没创建过
openfile, _ = os.Create(name)
namemap[name] = openfile
}
encoder := json.NewEncoder(openfile)
//往该文件写入数据
for k := i; k < j; k++ {
encoder.Encode(intermediate[i])
// fmt.Fprintf(openfile, "%v %v\n", intermediate[i].Key, 1)
}
i = j
}
for _, openfile := range namemap {
openfile.Close()//关闭文件
}
}
Reduce任务处理
func HandReduce(reducef func(string, []string) string, files []string, taskid int) {
fmt.Println("执行任务", taskid, files)
outname := "mr-out-" + strconv.Itoa(taskid)
outfile, _ := os.Create(outname)
intermediate := []KeyValue{}
for _, file := range files {
openfile, _ := os.Open(file)
decoder := json.NewDecoder(openfile)
for {
kv := KeyValue{}
if err := decoder.Decode(&kv); err != nil {
if err.Error() != "EOF" {
fmt.Println("读取键值对失败")
}
break
}
intermediate = append(intermediate, kv)
}
openfile.Close()
}
//下面代码源代码就有
sort.Sort(ByKey(intermediate))
i := 0
for i < len(intermediate) {
j := i + 1
for j < len(intermediate) && intermediate[j].Key == intermediate[i].Key {
j++
}
values := []string{}
for k := i; k < j; k++ {
values = append(values, intermediate[k].Value)
}
output := reducef(intermediate[i].Key, values)
fmt.Fprintf(outfile, "%v %v\n", intermediate[i].Key, output)
i = j
}
fmt.Println("任务执行完成", taskid, files)
outfile.Close()
}
最后
前置知识里go语言我只写了自己不懂的并且容易忘记的知识,还有论文部分我只针对这次实验简略概括了一下,详细的学习还是要自己读论文,看go的语法才行。
资料
MapReduce论文
Go
MIT6.5840 Lab1主页
来源链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Moyoj/p/18776683
如有侵犯您的版权,请及时联系3500663466#qq.com(#换@),我们将第一时间删除本站数据。








暂无评论内容