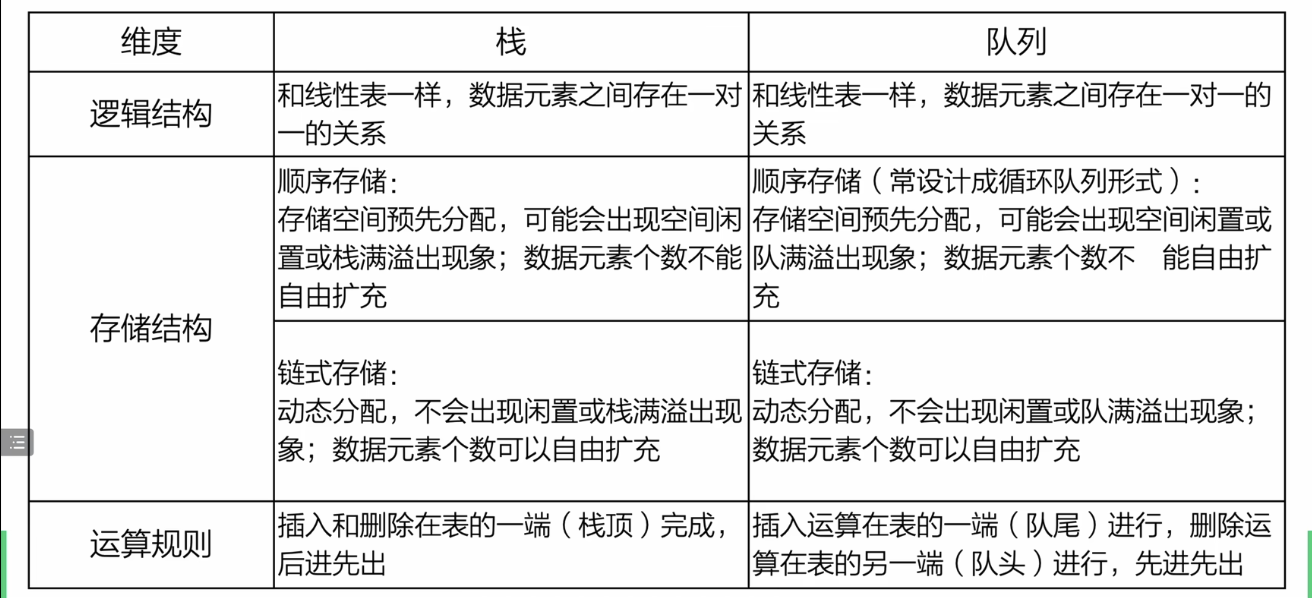
栈与队列
栈(stack)
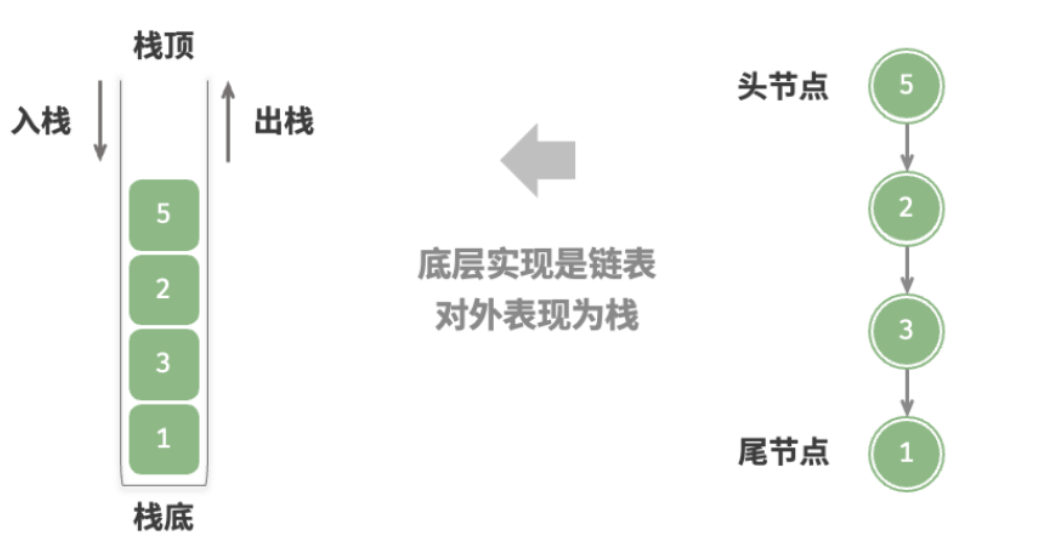
类比成一摞盘子,最上面的盘子就是栈顶,最下面的就是栈底。把元素添加到栈顶是入栈,删除栈顶就是出栈。
“先入后出”
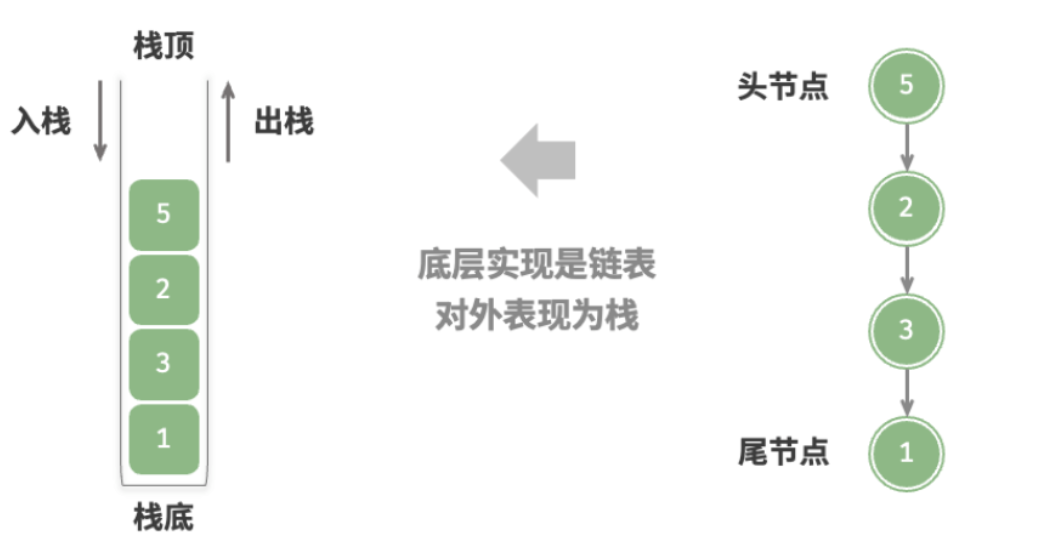
顺序实现
栈的结构
#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct {
ElemType data[MAXSIZE];
int top;
} Stack;
栈的初始化
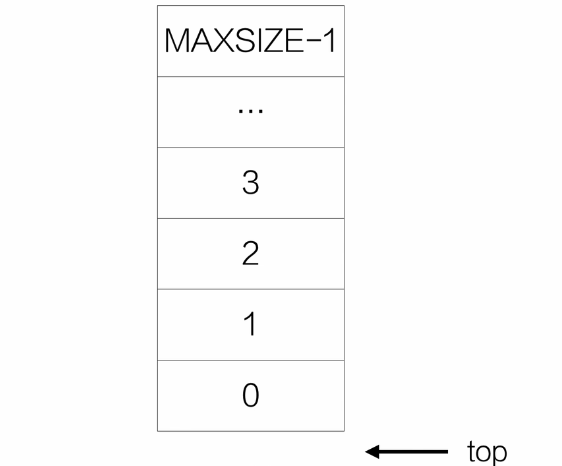
// 初始化栈
void initStack(Stack *s) {
s->top = -1;
}
栈的常用操作

入栈
//入栈
int push(Stack *s, ElemType e){
if(s->top == MAXSIZE-1){
printf("栈满\n");
return 0;
}
s->top++;
//从栈顶入栈
s->data[s->top] = e;
return 1;
}
出栈
//出栈
ElemType pop(Stack *s,ElemType *e){
if(s->top == -1){
printf("栈空\n");
return 0;
}
*e = s->data[s->top];
s->top--;
return *e;
}
查看栈顶元素
//查看栈顶元素
ElemType getTop(Stack *s,ElemType *e){
if(s->top == -1){
printf("栈空\n");
return 0;
}
*e = s->data[s->top];
return *e;
}
int main(){
Stack s;
initStack(&s);
push(&s,1);
push(&s,2);
push(&s,3);
ElemType elem;
getTop(&s,&elem);
printf("栈顶元素:%d\n",elem);
pop(&s,&elem);
printf("出栈元素:%d\n",elem);
printf("栈顶元素:%d\n",getTop(&s,&elem));
return 0;
}
顺序表_动态分配
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct {
ElemType *data;
int top;
} Stack;
// 初始化栈
Stack* initStack() {
Stack *s = (Stack*)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
s->data = (ElemType*)malloc(MAXSIZE * sizeof(ElemType));
s->top = -1;
return s;
}
//入栈
int push(Stack *s, ElemType e){
if(s->top == MAXSIZE-1){
printf("栈满\n");
return 0;
}
s->top++;
//从栈顶入栈
s->data[s->top] = e;
return 1;
}
//出栈
ElemType pop(Stack *s,ElemType *e){
if(s->top == -1){
printf("栈空\n");
return 0;
}
*e = s->data[s->top];
s->top--;
return *e;
}
//查看栈顶元素
ElemType getTop(Stack *s,ElemType *e){
if(s->top == -1){
printf("栈空\n");
return 0;
}
*e = s->data[s->top];
return *e;
}
int main(){
Stack *s = initStack();
push(s,1);
push(s,2);
push(s,3);
ElemType elem;
getTop(s,&elem);
printf("栈顶元素:%d\n",elem);
pop(s,&elem);
printf("出栈元素:%d\n",elem);
printf("栈顶元素:%d\n",getTop(s,&elem));
free(s->data);
free(s);
return 0;
}
链式实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct Stack{
ElemType data;
struct Stack *next;
}Stack;
Stack* initStack(){
Stack *s = (Stack*)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
s->next = NULL;
return s;
}
//判断栈是否为空
bool isEmpty(Stack *s){
return s->next == NULL;
}
//入栈
//头插法
int push(Stack *s, ElemType e){
Stack *p = (Stack*)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
p->data = e;
p->next = s->next;
s->next = p;
return 1;
}
//出栈
//删去头结点的next
ElemType pop(Stack *s, ElemType *e){
if(s->next == NULL){
printf("栈为空!\n");
return 0;
}
*e = s->next->data;
Stack *p = s->next;
s->next = p->next;
free(p);
return *e;
}
//获取栈顶元素
ElemType getTop(Stack *s){
if(s->next == NULL){
printf("栈为空!\n");
return 0;
}
return s->next->data;
}
int main(){
Stack *s = initStack();
push(s,1);
push(s,2);
push(s,3);
printf("栈顶元素:%d\n",getTop(s));
ElemType elem;
pop(s,&elem);
printf("出栈元素:%d\n",elem);
printf("栈顶元素:%d\n",getTop(s));
free(s);
return 0;
}
队列(queue)
先入先出
入队:队尾入队
出队:队首出队
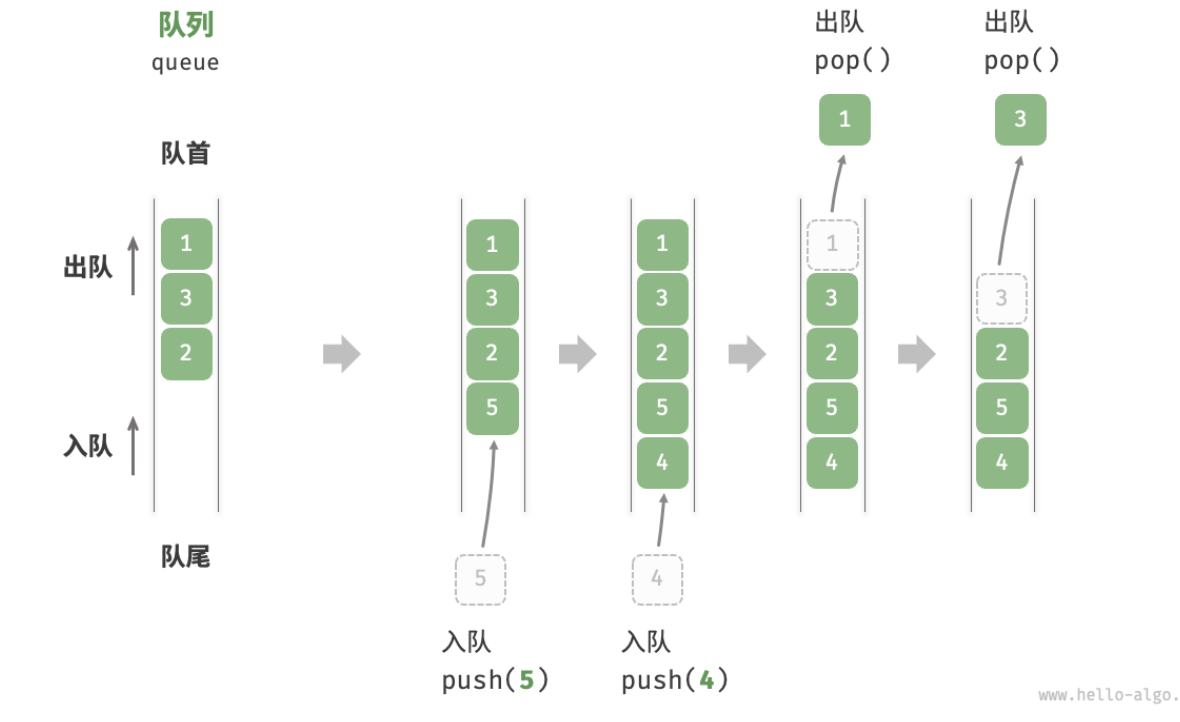
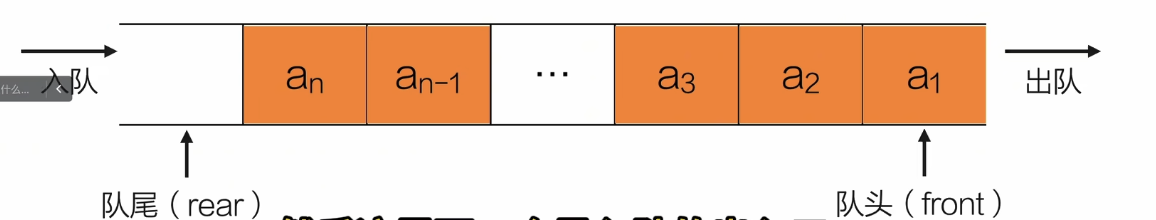
顺序实现
队列结构
#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct{
ElemType data[MAXSIZE];
int front, rear;
}Queue;
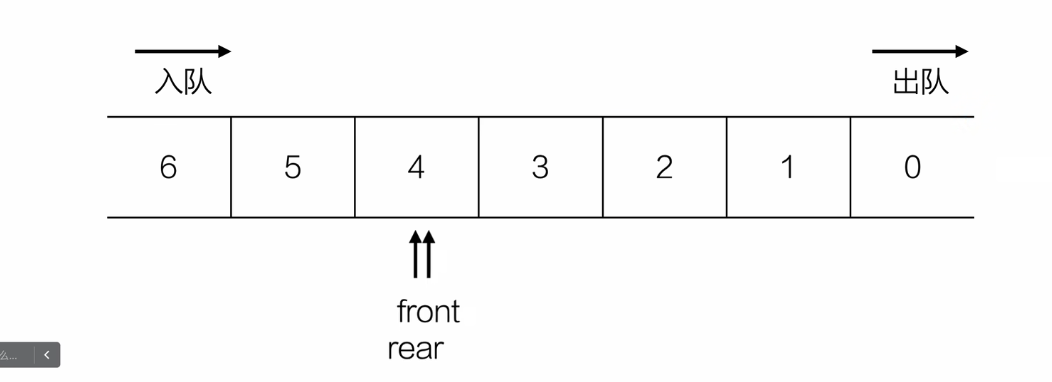
初始化
int initQueue(){
Queue *q = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
if(q == NULL){
return -1;
}
q->front = 0;
q->rear = 0;
return q;
}
判断是否为空
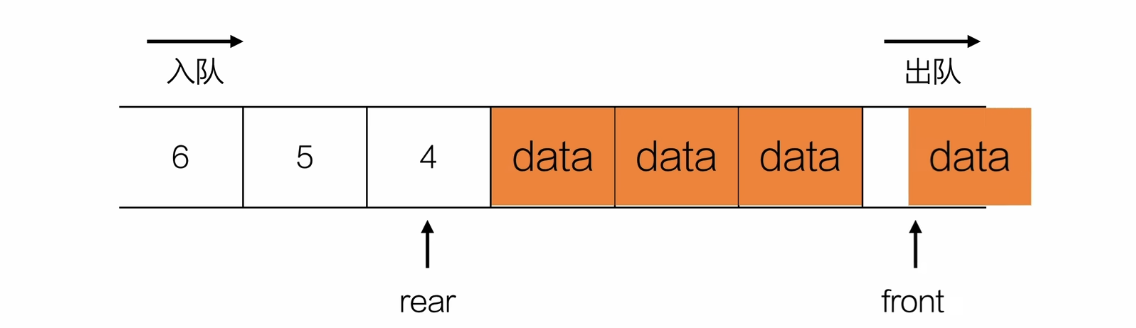
bool isEmpty(Queue *q){
return q->front == q->rear;
}
出队
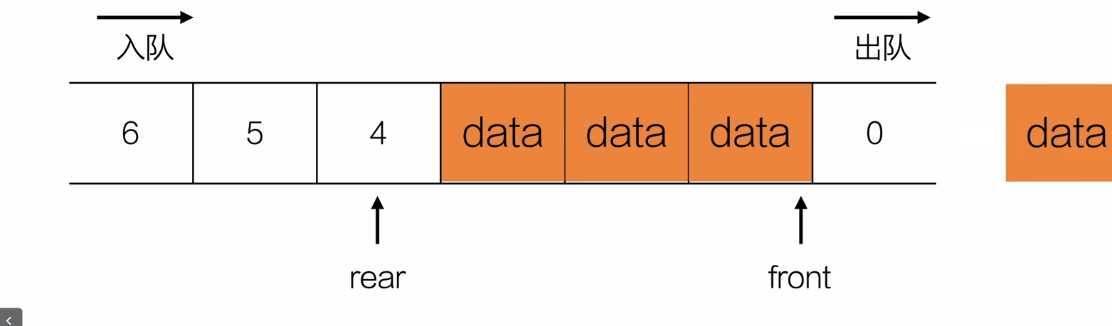
//出队
//从队首出队
ElemType pop(Queue *q,ElemType *e){
if(isEmpty(q)){
printf("队列为空!\n");
return -1;
}
*e = q->data[q->front];
q->front++;
return *e;
}
入队
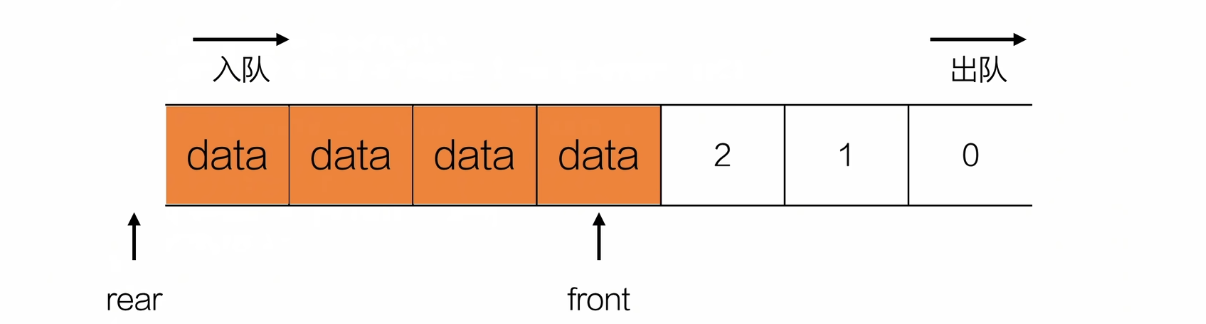
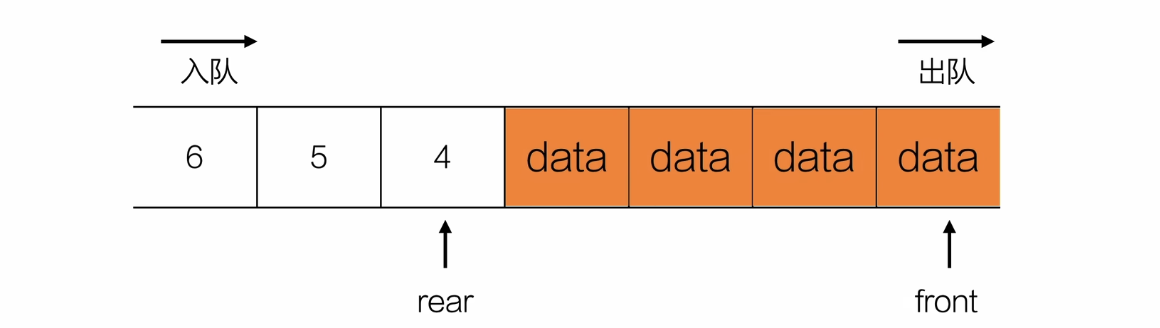
//队首是空
bool frontIsEmpty(Queue *q){
if(q->front == 0){
printf("队首不空\n");
return 0;
}
//队首索引不为0,说明前面有空的位置,需要挪过去
else{
int step = q->front;
for(int i = q->front;i <= q->rear;i++){
q->data[i-step] = q->data[i];
}
q->front = 0;
q->rear = q->rear - step;
return 1;
}
}
//入队
//从队尾入队
int push(Queue *q, ElemType e){
//队尾到头的情况下,队首不空,说明队列已满
if(q->rear == MAXSIZE-1 && !frontIsEmpty(q)){
printf("队列已满!\n");
return 0;
}
q->data[q->rear] = e;
q->rear++;
return 1;
}
获取队首元素
//获取队首元素
ElemType getFront(Queue *q){
if(isEmpty(q)){
printf("队列为空!\n");
return -1;
}
return q->data[q->front];
}
int main(){
Queue* q = initQueue();
push(q,1);
push(q,2);
push(q,3);
push(q,4);
printf("队首元素为:%d\n",getFront(q));
ElemType e;
pop(q,&e);
printf("出队元素为:%d\n",e);
pop(q,&e);
printf("出队元素为:%d\n",e);
return 0;
}
顺序实现_动态内存分配
只有结构体和初始化的区别,其他都一样
typedef struct
{
ElemType *data;
ElemType front, rear;
} Queue;
Queue *initQueue()
{
Queue *q = (Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
q->data = (ElemType *)malloc(MAXSIZE * sizeof(ElemType));
q->front = 0;
q->rear = 0;
return q;
}
循环队列
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// 最大容量
#define MAXSIZE 4
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType *data;
ElemType front, rear;
} Queue;
Queue *initQueue()
{
Queue *q = (Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
q->data = (ElemType *)malloc(MAXSIZE * sizeof(ElemType));
q->front = 0;
q->rear = 0;
return q;
}
int count = 0;
bool isEmpty(Queue *q)
{
return count == 0 && q->rear == q->front;
}
// 入队
// 从队尾入队
int push(Queue *q, ElemType e)
{
// 队列满的时候,rear+1 == MAXSIZE,因为rear和front都是从0开始计数的
if (count == MAXSIZE && (q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == q->front)
{
printf("队列已满!\n");
return -1;
}
q->data[q->rear] = e;
//更新rear索引
q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;
count++;
printf("当前的元素个数为:%d\n",count);
return 1;
}
// 出队
// 从队首出队
ElemType pop(Queue *q, ElemType *e)
{
if (isEmpty(q))
{
printf("队列为空!\n");
return -1;
}
*e = q->data[q->front];
//更新front索引
q->front = (q->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
count--;
printf("当前的元素个数为:%d\n",count);
return *e;
}
// 获取队首元素
ElemType getFront(Queue *q)
{
if (isEmpty(q))
{
printf("队列为空!\n");
return -1;
}
return q->data[q->front];
}
int main()
{
Queue *q = initQueue();
push(q, 1);
push(q, 2);
push(q, 3);
push(q, 4);
printf("队首元素为:%d\n", getFront(q));
ElemType e;
pop(q, &e);
printf("出队元素为:%d\n", e);
pop(q, &e);
printf("出队元素为:%d\n", e);
return 0;
}
定义一个count变量用来记录当前元素的总个数,防止循环队列总是存不满的情况
也就是下面的情况:
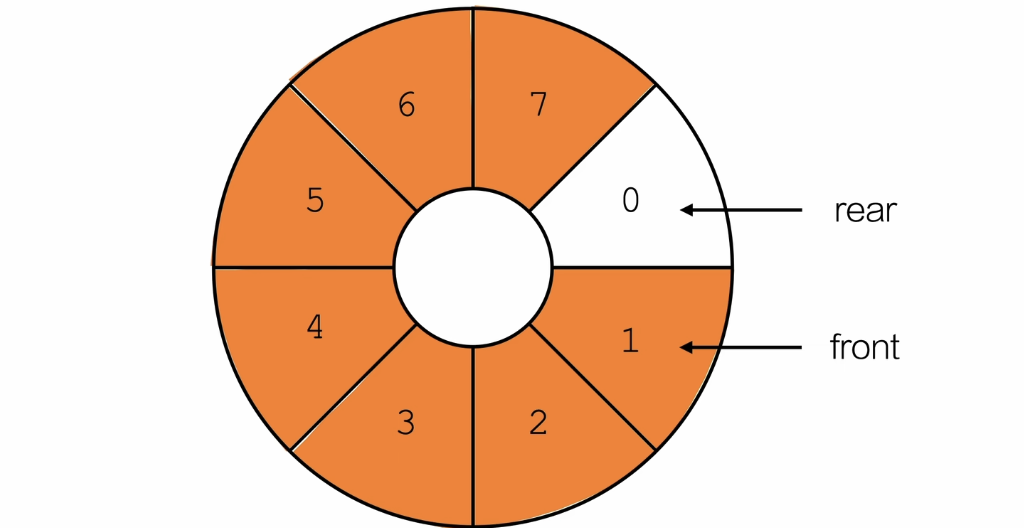
rear总是指向队尾的下一个索引,那么满队列判断的时候1==1,满了,但实际没满,所以再加一个变量count的判断
链式实现
队列结构
// 最大容量
typedef int ElemType;
// 队列节点
typedef struct QueueNode
{
ElemType data;
struct QueueNode *next;
} QueueNode;
// 队列
typedef struct{
QueueNode *front;
QueueNode *rear;
}Queue;
初始化
Queue* initQueue()
{
QueueNode *qNode = (QueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
qNode->data = 0;
qNode->next = NULL;
Queue *q = (Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
q->front = qNode;
q->rear = qNode;
return q;
}
队列是否空
// 队列是否为空
bool isEmpty(Queue *q)
{
return q->rear == q->front;
}
入队
尾插法
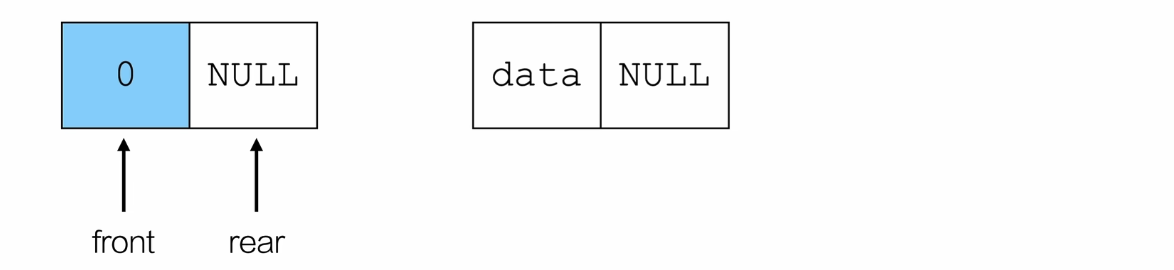
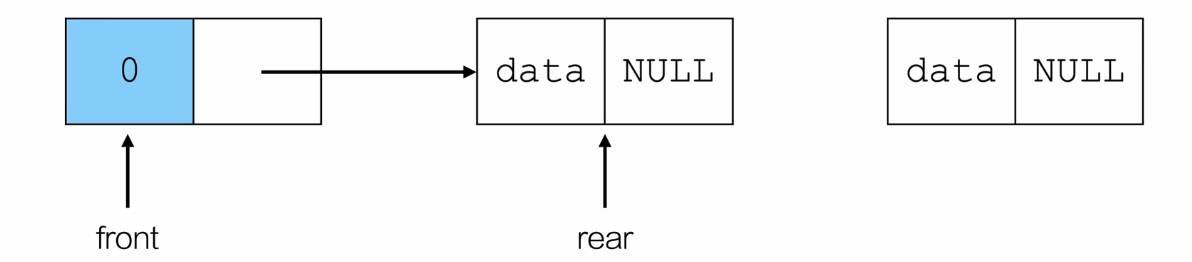
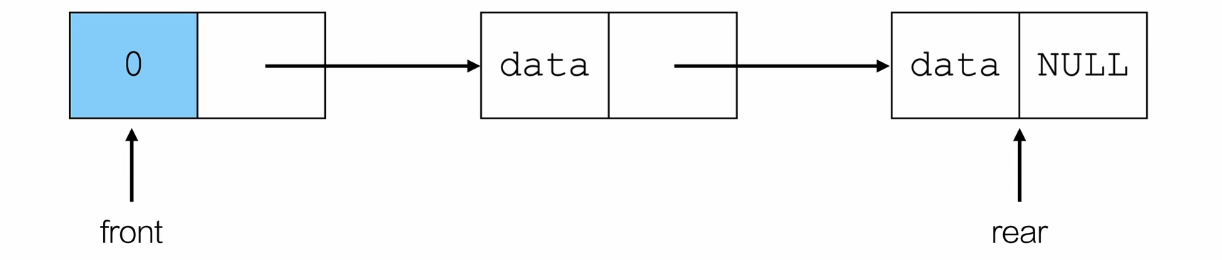
// 入队
// 从队尾入队
// 尾插法
int push(Queue *q, ElemType e)
{
QueueNode *qNode = (QueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
qNode->data = e;
qNode->next = NULL;
//插在尾节点的next
q->rear->next = qNode;
q->rear = qNode;
return 1;
}
出队
// 出队
// 从队首出队
ElemType pop(Queue *q, ElemType *e)
{
QueueNode *qnode = q->front->next;
*e = qnode->data;
q->front->next = qnode->next;
if(q->rear == qnode){
q->rear = q->front;
}
free(qnode);
return *e;
}
队首元素
// 获取队首元素
ElemType getFront(Queue *q)
{
if (isEmpty(q))
{
printf("队列为空!\n");
return -1;
}
return q->front->next->data;
}
int main()
{
Queue *q = initQueue();
push(q, 1);
push(q, 2);
push(q, 3);
push(q, 4);
printf("队首元素为:%d\n", getFront(q));
ElemType e;
pop(q, &e);
printf("出队元素为:%d\n", e);
pop(q, &e);
printf("出队元素为:%d\n", e);
return 0;
}
双端队列
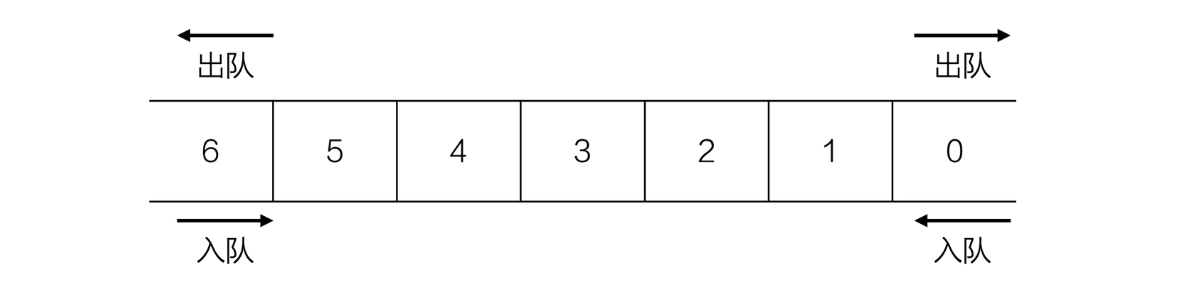
习题1

选c
习题2

选d
习题3

选c
习题4

4个
dcbae
dcbea
dceba
decba
习题5
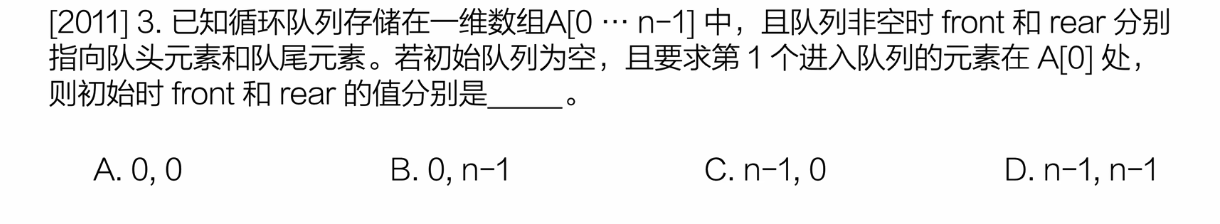
入队更新:
front指向队头
rear = (rear+1)%MAXSIZE
下面对每个选项进行验证,注意初始为空队列,front==rear:
a. rear递增后为1,错误
d.rear递增后为0,正确
选d
习题6

只有3不可能,n-1
习题7

选a
循环队列,队空条件: front == rear, 队满条件: front == (rear+1)%MAXSIZE
习题8
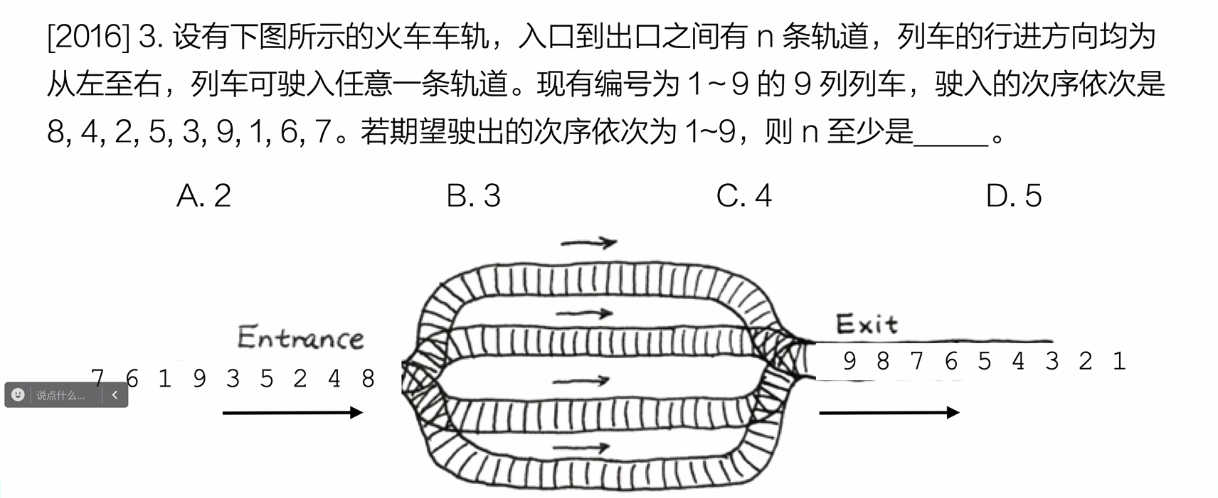
队列
98
7654
32
1
选c
习题9

入栈次序不能决定出栈顺序,栈不能两端操作,选c
习题10

注意栈顶位置
5 8 3 2(top) 2+3
8 3 2 5(top) 5-2
3 2 5 3(top) 3*5
2 5 3 15(top)
习题11

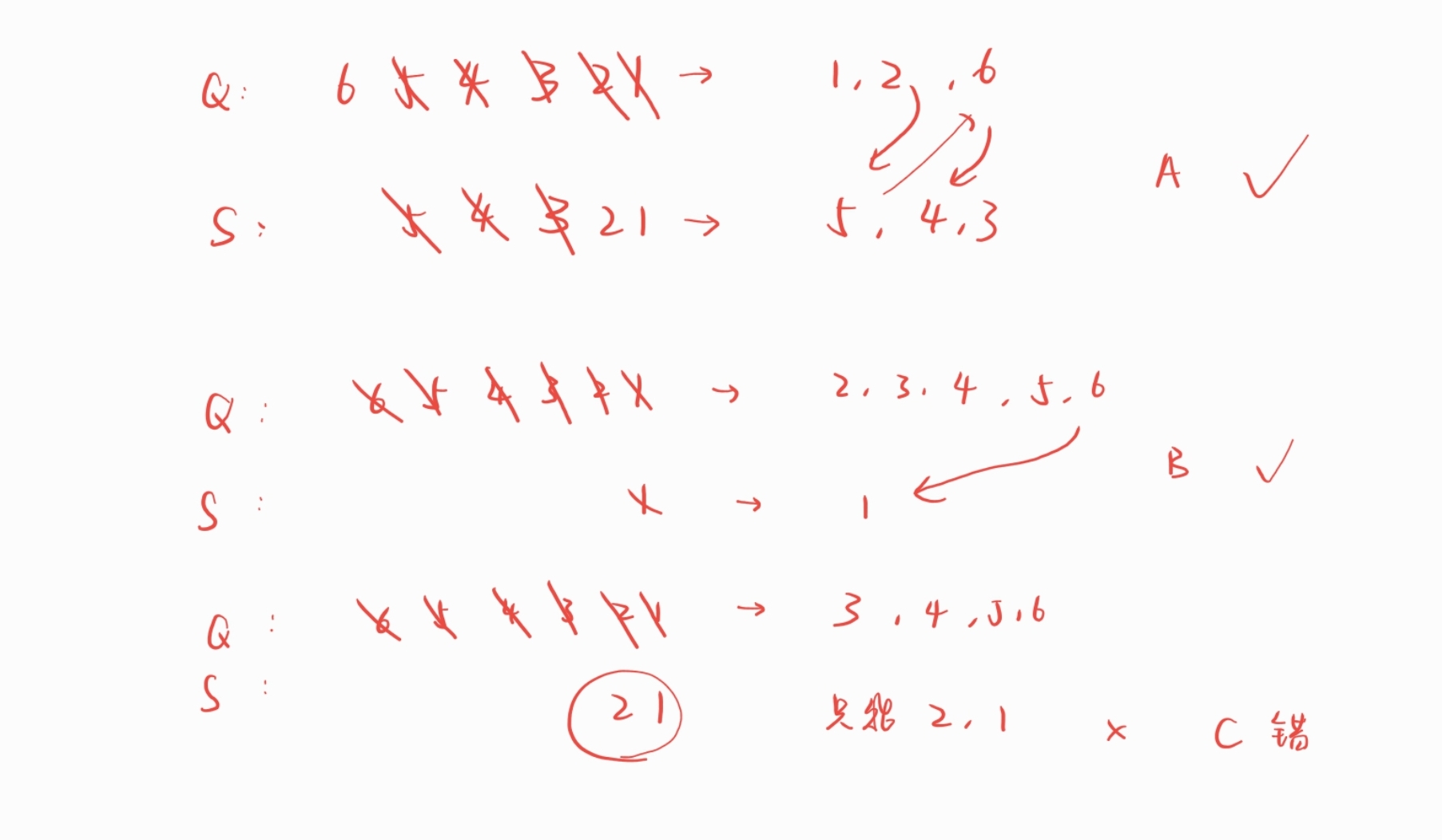
选c
习题12

选d
总结
来源链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/eanojiang/p/18824723





没有回复内容